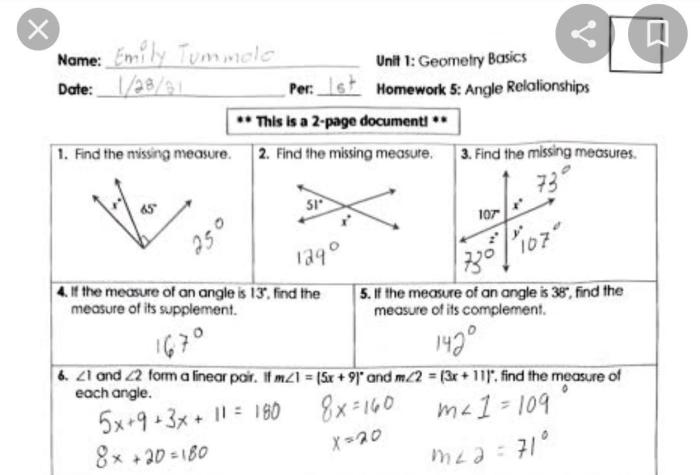
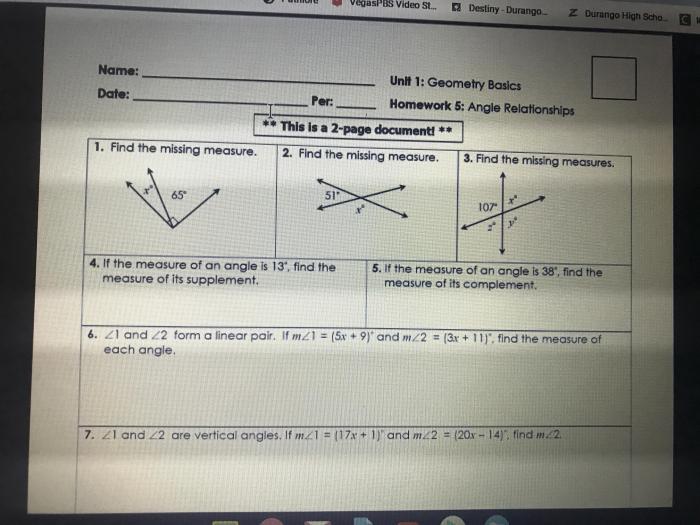
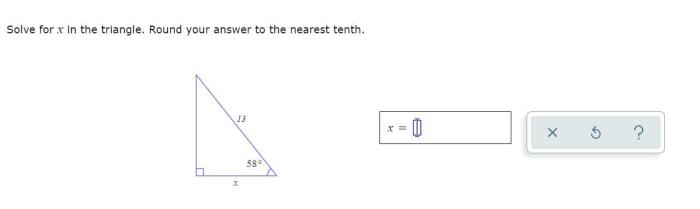
Unit 1 geometry basics homework 3 angle relationships answer key – Embark on a journey through the realm of geometry with Unit 1 Geometry Basics Homework 3: Angle Relationships Answer Key. This comprehensive guide unlocks the secrets of angle measurement, theorems, and properties, empowering you to conquer any geometry challenge.
Delve into the intricacies of complementary, supplementary, vertical, and adjacent angles, gaining a deep understanding of their relationships. Master the art of angle measurement using a protractor and explore the diverse units of angle measurement. Unravel the Angle Bisector Theorem, Angle Sum Theorem, and more, unlocking the power of geometry to solve complex problems.
Unit 1: Geometry Basics Homework 3: Angle Relationships: Unit 1 Geometry Basics Homework 3 Angle Relationships Answer Key
Angle relationships are fundamental concepts in geometry that describe the positions and interactions of angles. Understanding these relationships is essential for solving geometry problems and comprehending geometric shapes and structures.
Angle Relationships
Angle relationships refer to the various ways in which angles can be related to each other. The main types of angle relationships include:
- Complementary angles: Two angles that add up to 90 degrees.
- Supplementary angles: Two angles that add up to 180 degrees.
- Vertical angles: Two angles that are opposite each other and share a common vertex.
- Adjacent angles: Two angles that share a common vertex and a common side.
Angle Measurement
Measuring angles accurately is crucial in geometry. Angles are typically measured using a protractor, a tool that has a graduated scale and two arms that meet at a vertex.
The standard unit of angle measurement is the degree, denoted by the symbol °. One degree is defined as 1/360 of a full rotation. Other units of angle measurement include radians and gradians.
Angle Theorems, Unit 1 geometry basics homework 3 angle relationships answer key
Angle theorems are geometric theorems that describe relationships between angles. Some of the most important angle theorems include:
- Angle Bisector Theorem: If a ray bisects an angle, then it divides the angle into two congruent angles.
- Angle Sum Theorem: The sum of the interior angles of a polygon with n sides is (n – 2) – 180 degrees.
Angle Properties
Angles possess certain properties that can be used to solve geometry problems. Some of the key angle properties include:
- Angles on a straight line add up to 180 degrees.
- Angles in a triangle add up to 180 degrees.
Angle Relationships in Special Quadrilaterals
Special quadrilaterals, such as squares, rectangles, and parallelograms, have specific angle relationships.
- In a square, all four angles are right angles (90 degrees).
- In a rectangle, opposite angles are congruent and adjacent angles are supplementary.
- In a parallelogram, opposite angles are congruent and adjacent angles are supplementary.
Angle Relationships in Circles
Circles also have specific angle relationships.
- A central angle is an angle whose vertex is at the center of the circle.
- An inscribed angle is an angle whose vertex is on the circle and whose sides intersect the circle.
FAQ Insights
What is the Angle Sum Theorem?
The Angle Sum Theorem states that the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180 degrees.
How do I measure an angle using a protractor?
Place the center of the protractor on the vertex of the angle and align the baseline with one of the rays. Read the angle measurement where the other ray intersects the protractor’s scale.
What is the difference between complementary and supplementary angles?
Complementary angles add up to 90 degrees, while supplementary angles add up to 180 degrees.