The diagnostic term for the fungal infection candid/iasis literally means – The diagnostic term “candidiasis” literally means “infection caused by Candida,” a genus of fungi. This term reflects the close relationship between the fungal infection and the organism that causes it. Candidiasis can affect various body systems, ranging from the skin and nails to the bloodstream and internal organs.
Throughout history, candidiasis has been recognized and studied, leading to the development of diagnostic methods and treatment strategies. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the etymology, historical context, clinical significance, diagnostic approaches, treatment options, epidemiology, and prevention of candidiasis, providing a thorough understanding of this prevalent fungal infection.
Etymology of Candidiasis: The Diagnostic Term For The Fungal Infection Candid/iasis Literally Means
The term “candidiasis” originates from the Latin word “candidus,” which literally means “white” or “shining.” This etymology reflects the characteristic white or cream-colored appearance of Candida colonies when grown on culture media. The fungal infection caused by Candida species is known as candidiasis, and the term accurately describes the visual manifestation of the infection.
Historical Context of Candidiasis
Candidiasis has been recognized for centuries, with early descriptions of the infection dating back to the 16th century. In the late 19th century, the causative agent was identified as a fungus, and the term “monilia” was initially used to refer to the infection.
In the early 20th century, the term “candidiasis” became more widely adopted, reflecting the increasing understanding of the infection and its fungal etiology.
Clinical Significance of Candidiasis
Candidiasis can manifest in a variety of clinical presentations, ranging from superficial infections of the skin and mucous membranes to invasive systemic infections. Common types of candidiasis include oral thrush, vaginal yeast infections, and invasive candidiasis, which can affect various organs and tissues.
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial to prevent complications and ensure optimal patient outcomes.
Diagnostic Methods for Candidiasis
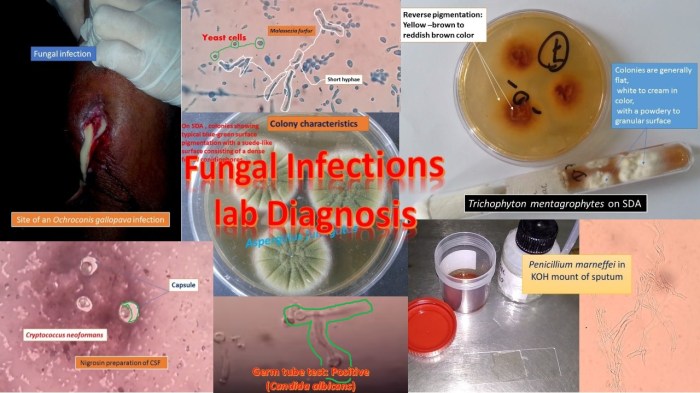
The diagnosis of candidiasis relies on laboratory techniques to identify the presence of Candida species. Microscopy and culture are traditional methods, while molecular diagnostic techniques offer rapid and specific identification. Microscopy allows for the visualization of Candida cells, while culture involves growing the fungus on selective media to confirm its presence.
Molecular methods, such as PCR and sequencing, enable the identification of specific Candida species and detection of resistance genes.
Treatment Options for Candidiasis
The treatment of candidiasis involves the use of antifungal medications to eradicate the fungal infection. Antifungals are classified into different groups based on their mechanism of action and target site. Common antifungal classes include azoles, echinocandins, and polyenes. The choice of treatment regimen depends on the type of candidiasis, severity of infection, and susceptibility of the Candida species to specific antifungals.
Epidemiology and Prevention of Candidiasis

Candidiasis is a common fungal infection worldwide, with varying prevalence rates depending on geographic region and healthcare settings. Risk factors for candidiasis include immunosuppression, diabetes, prolonged antibiotic use, and indwelling medical devices. Preventive measures to reduce the risk of candidiasis include maintaining good hygiene, avoiding unnecessary antibiotic use, and implementing infection control practices in healthcare settings.
General Inquiries
What are the common symptoms of candidiasis?
Symptoms vary depending on the location of the infection but may include itching, redness, discharge, pain, and discomfort.
How is candidiasis diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves physical examination, microscopy, culture, and molecular diagnostic methods to identify Candida species.
What are the treatment options for candidiasis?
Treatment typically involves antifungal medications, with the choice of regimen depending on the type and severity of the infection.
How can candidiasis be prevented?
Preventive measures include maintaining good hygiene, managing underlying medical conditions, and avoiding unnecessary antibiotic use.